I have decided to dedicate a special text to the problematics of intraabdominal fluid. Intraperitoneal fluid is present by ascites, inflammations, tumours and after traumas (blood).
Fluid (no matter its etiology) appears as an anechogenic (black) area. Under normal circumstances it is located only in blood vessels (blood), in gallbladder and bile ducts (bile) and in urinary tract and bladder (urine).
Ascites – We often find it around liver and spleen. Sometimes these organs „swim“ in ascitic fluid. Extensive ascites is diffuse and is well seen in contrast with hyperechogenic intestinal loops floating in the black ascitic fluid.
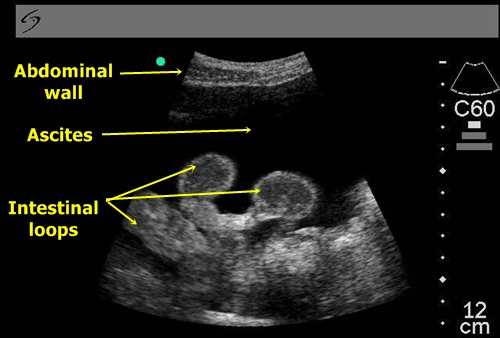
Ascites – Intestinal loops in ascitic fluid

Ascites – Ascitic fluid around the liver tissue
Fluid in Douglas pouch – Douglas pouch by a woman is the deepest intraperitoneal area. It is located between uterus and rectum. Fluid in this area is found in inflammations and intraabdominal tumours. It is a very important finding by patients after traumas (intraperitoneal blood). The fluid is visible behind the urinary bladder and uterus and in front of the rectum. By males analogical area is between the urinary bladder and rectum.
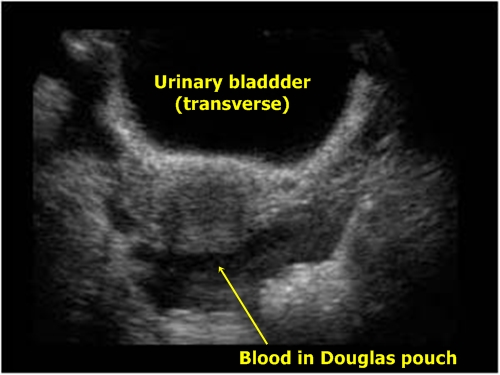
Fluid in Douglas pouch – It is not very clearly
visible, sagittal cut would be surely better
Fluid in Morrison‘s pouch – Morrison’s pouch is a peritoneal prominence which could be easily located in sagittal plane between liver tissue and right kidney. The fluid could be a classic ascites, blood after traumas or fluid by acute pancreatitis.
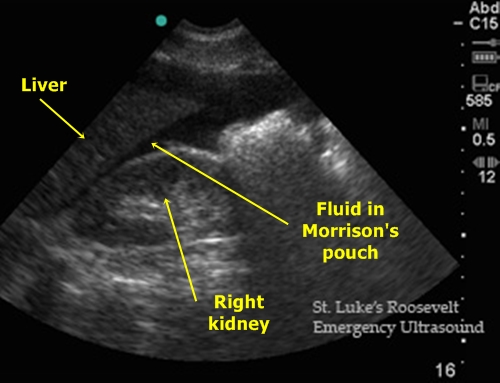
Fluid in Morrison’s pouch
Fluid near gallbladder – Fluid between gallbladder and liver tissue is often found by acute cholecystitis as so-called pericholecystitis.
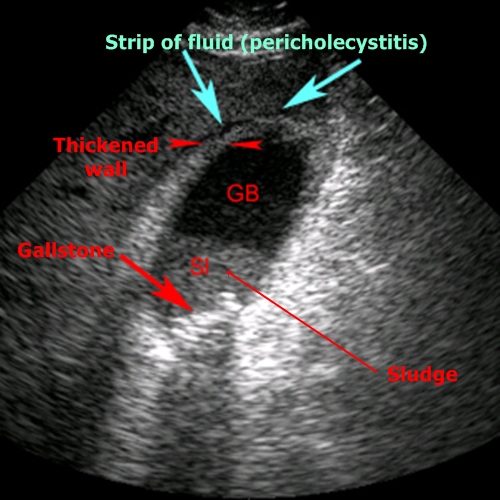
Fluid near gallbladder – Thickened wall and pericholecystitis
are clear signs of acute cholecystitis.
Splenic subcapsular fluid – It often follows splenic traumas and we find it typically near upper medial pole of the spleen.
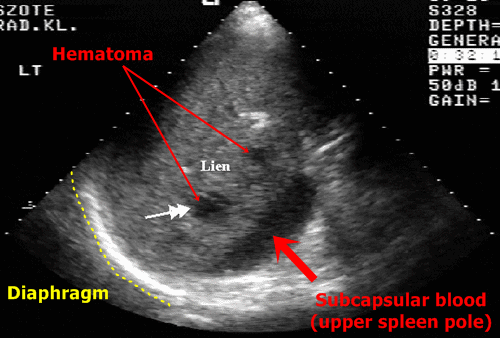
Splenic subcapsular fluid - Near the upper splenic
pole with a close relation to the diaphragm
Fluid near pancreas - It is typically connected with acute pancreatitis
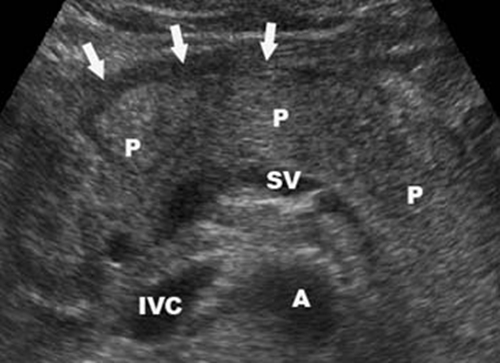
Fluid near pancreas – A stripe of fluid in front of
pancreatic tissue marked by white arrows



